Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients critical for human health. From supporting cardiovascular health to enhancing brain function and reducing inflammation, their benefits are profound and far-reaching. In this article, we will explore every aspect of their impact on health, providing practical tips and insights for incorporating them into your lifestyle.
 |
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat, often referred to as "essential fats" because the body cannot produce them. These fats must be obtained through dietary sources or supplementation. The three main types of Omega-3 fatty acids are:
- Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA): Found in plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and canola oil. ALA is primarily used as an energy source but can be converted into EPA and DHA in small amounts.
- Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA): Found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and herring. EPA is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
- Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA): Found in marine sources, DHA is essential for brain and eye health, playing a significant role in neural and retinal function.
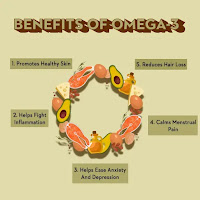
Comprehensive Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
1. Cardiovascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids are widely recognized for their ability to improve heart health. Regular intake has been shown to:
- Lower triglyceride levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Regulate blood pressure, particularly in individuals with hypertension.
- Enhance arterial flexibility, supporting better blood flow.
- Prevent blood clots, lowering the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
In fact, studies have demonstrated that people who consume higher amounts of Omega-3 have a significantly lower risk of developing heart disease compared to those with low intake.
2. Brain Function and Mental Health
DHA, a critical component of brain tissue, is essential for cognitive development and neural function. Omega-3s can help:
- Improve memory, focus, and learning capabilities.
- Reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and dementia.
- Alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, with EPA playing a crucial role in mood regulation.
For pregnant women, Omega-3s support fetal brain development, leading to better cognitive outcomes for their children.
3. Anti-inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation is a silent cause of many health issues, including arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease. Omega-3 fatty acids are powerful anti-inflammatory agents that:
- Reduce joint pain and stiffness in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Lower inflammation in blood vessels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular conditions.
- Mitigate the inflammatory response in autoimmune diseases.
4. Eye Health
DHA is a structural component of the retina and plays a critical role in maintaining vision. Omega-3s:
- Reduce the risk of macular degeneration, a leading cause of blindness in older adults.
- Alleviate dry eye syndrome by improving tear production and eye lubrication.
5. Skin Health
Omega-3s improve skin texture and elasticity. They also help manage conditions such as:
- Psoriasis by reducing redness and scaling.
- Eczema by alleviating itching and dryness.
By strengthening the skin’s barrier, Omega-3s also help retain moisture and protect against sun damage.
6. Maternal and Infant Health
For expecting mothers, Omega-3s are essential for the development of the baby’s brain, eyes, and nervous system. They also help:
- Reduce the risk of preterm labor.
- Lower the likelihood of postpartum depression.
7. Bone and Joint Health
Omega-3 fatty acids increase calcium absorption in bones and reduce bone breakdown. This makes them beneficial for preventing osteoporosis and reducing joint pain associated with arthritis.
8. Weight Management
Omega-3s play a role in weight management by:
- Boosting metabolism and increasing fat burning.
- Reducing appetite and helping control cravings.
9. Supports Immune Function
Omega-3s enhance the immune system by reducing chronic inflammation and improving the body’s ability to fight infections.
10. Helps Prevent Cancer
Preliminary research suggests that Omega-3s may help prevent certain types of cancer, including colon, prostate, and breast cancer, by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells.
Best Dietary Sources of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Incorporate these foods into your diet to boost Omega-3 intake:
- Fatty fish: salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna.
- Plant-based sources: flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds.
- Fortified foods: Omega-3 enriched eggs and dairy products.
- Algae oil: A vegan source of DHA and EPA.
How to Incorporate Omega-3s into Your Diet
Here are practical tips for including Omega-3s in your meals:
- Add flaxseeds or chia seeds to smoothies and salads.
- Prepare meals with fatty fish at least twice a week.
- Snack on a handful of walnuts or almonds daily.
- Choose fortified products such as milk or cereal with added Omega-3s.
What are the health benefits of Omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that provide a range of health benefits. They play a crucial role in brain function, reduce inflammation, support heart health, and are vital for cell structure. Omega-3s are beneficial for maintaining cognitive function, lowering the risk of heart disease, improving joint health, and promoting mental well-being.
Can Omega-3 fatty acids help with heart disease?
Yes, Omega-3 fatty acids are widely known for their positive effects on heart health. They help lower triglyceride levels, reduce blood pressure, and improve overall cardiovascular health by decreasing inflammation in the body. Regular consumption of Omega-3s can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
What foods are rich in Omega-3 fatty acids?
Foods rich in Omega-3 fatty acids include fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. Other good sources are flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds. Additionally, fortified foods such as certain brands of eggs and dairy products also contain Omega-3s. For plant-based sources, algae supplements are a great option.
Can Omega-3 fatty acids improve brain health?
Yes, Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in brain health by supporting cognitive function and protecting against mental decline. DHA, a type of Omega-3, is a major structural component of the brain. Consuming sufficient Omega-3s has been linked to improved memory, mood regulation, and a reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
How can Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation?
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce chronic inflammation in the body. They do this by influencing the production of eicosanoids, which are hormone-like substances that regulate inflammation. By reducing inflammation, Omega-3s may alleviate symptoms of conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Are there any side effects of taking Omega-3 supplements?
Omega-3 supplements are generally considered safe when taken in recommended amounts. However, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as fishy aftertaste, gastrointestinal discomfort, or nausea. To minimize these side effects, it is advised to take supplements with meals. In rare cases, excessive Omega-3 intake can lead to bleeding or affect blood clotting, so it's important to consult a healthcare provider before starting high-dose supplements.
How much Omega-3 should I consume daily?
The recommended daily intake of Omega-3 fatty acids varies depending on age, gender, and health conditions. For general health, the American Heart Association recommends eating at least two servings of fatty fish per week, which is approximately 500-1000 mg of EPA and DHA (two main types of Omega-3s) daily. For specific health concerns such as high cholesterol or inflammation, higher doses may be recommended, but it’s important to consult a healthcare professional.
Can I get enough Omega-3 from a vegetarian diet?
Yes, vegetarians can obtain Omega-3 fatty acids from plant-based sources. The primary type of Omega-3 in plants is ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), found in flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and canola oil. However, the body must convert ALA into the more beneficial forms of Omega-3s, EPA and DHA, which is less efficient than directly consuming EPA and DHA from fish or algae-based supplements. Algal oil is a good vegan source of DHA and EPA.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can vegetarians meet their Omega-3 needs?
Yes, plant-based sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts provide ALA. Algae oil supplements are an excellent source of DHA and EPA for vegetarians and vegans.
2. How much Omega-3 do I need daily?
Most health organizations recommend 250-500 mg of EPA and DHA combined daily for adults.
Omega-3 fatty acids are a cornerstone of a healthy diet. Regular consumption can lead to a healthier heart, sharper mind, and stronger body. Start incorporating these essential fats into your meals today for long-term health benefits.
Omega-3 benefits, Omega-3 health benefits, Omega-3 fatty acids, heart health, brain health, Omega-3 anti-inflammatory, Omega-3 supplements, Omega-3 foods, DHA, EPA